Student characteristics associated with interpersonal skills in medical consultations - BMC Medical Education
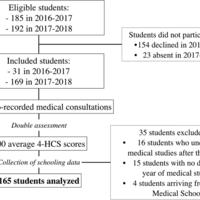
Background The quality of medical care depends on effective physician–patient communication. Interpersonal skills can be improved through teaching, but the determinants are poorly understood. We therefore assessed the factors associated with the interpersonal skills of medical students during simul…